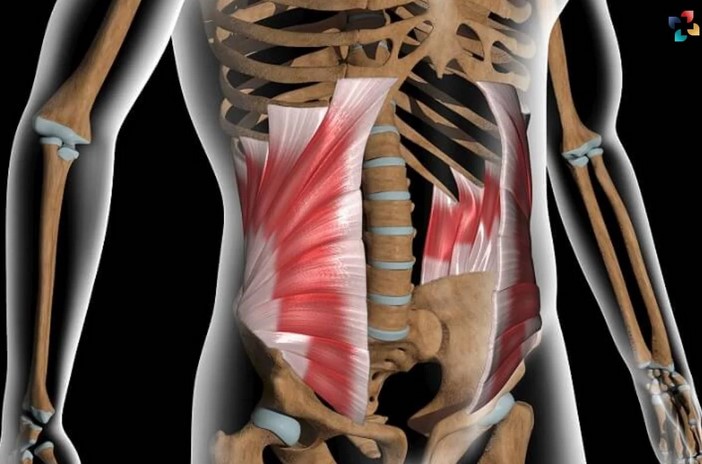
The Internal Abdominal Oblique Muscle is one of the muscles in the abdominal wall, located just inside the external oblique muscle. It originates from the lumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament, and inserts into the inferior borders of the 10th through 12th ribs, linea alba, and pubic crest. This muscle plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including forced respiration, aiding in urination and defecation, trunk rotation, and lateral flexion of the spine. It also helps maintain abdominal wall tension and supports the abdominal viscera.
Understanding the Internal Abdominal Oblique Muscle: Anatomy and Function
The internal abdominal oblique muscle, often simply referred to as the internal oblique, is a crucial component of the human muscular system. This muscle, located within the abdominal region, plays a pivotal role in various bodily functions, including respiration, posture, and protection of internal organs. Understanding the anatomy and function of the internal abdominal oblique muscle can provide valuable insights into the complex workings of the human body.
The internal abdominal oblique muscle is one of the four major muscles that constitute the abdominal wall. It is situated in the lateral and anterior parts of the abdomen, beneath the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle. The muscle fibers of the internal oblique run diagonally from the lower ribs to the pelvis, creating a kind of crisscross pattern. This unique arrangement of muscle fibers allows the internal oblique to perform a variety of movements and functions.
One of the primary functions of the internal abdominal oblique muscle is to aid in respiration. During exhalation, the muscle contracts, reducing the volume of the thoracic cavity and forcing air out of the lungs. Conversely, during inhalation, the muscle relaxes, allowing the thoracic cavity to expand and air to flow into the lungs. This rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the internal oblique muscle is a vital part of the respiratory process.
In addition to its role in respiration, the internal abdominal oblique muscle also contributes significantly to maintaining posture. The muscle provides stability to the trunk, enabling us to stand upright and perform various physical activities. It also assists in flexing the spine, allowing us to bend forward, and in lateral flexion, enabling us to bend sideways. Moreover, the internal oblique muscle plays a role in rotation of the trunk, allowing us to twist our bodies.
The internal abdominal oblique muscle also serves a protective function. It forms part of the body’s natural armor, shielding the internal organs within the abdominal cavity from potential harm. By contracting, the muscle can increase intra-abdominal pressure, providing additional support and protection to the organs during strenuous physical activities.
Furthermore, the internal oblique muscle plays a role in various other bodily functions. For instance, it assists in the process of urination and defecation by increasing intra-abdominal pressure. It also contributes to the process of childbirth, where it aids in pushing the baby out during labor.
In conclusion, the internal abdominal oblique muscle, with its unique anatomy and diverse functions, is an integral part of the human muscular system. It not only aids in vital processes such as respiration and posture maintenance but also serves a protective role, safeguarding the internal organs. Understanding the anatomy and function of this muscle can enhance our appreciation of the intricate design and workings of the human body.The Internal Abdominal Oblique Muscle is a crucial component of the human muscular system, playing a significant role in respiration, posture, and overall core stability. It is located in the abdominal region, beneath the external obliques. Its primary functions include aiding in forced respiration, assisting in the rotation and lateral flexion of the spine, and contributing to abdominal compression. Therefore, the health and strength of this muscle are vital for maintaining proper body mechanics and functionality.